How to Build an MVP
Sep 06, 2023
In the fast-paced world of startups, time and resources are of the essence. Developing a full-fledged product without knowing if there's a demand for it can be a risky and expensive endeavor. This is where the concept of the Minimum Viable Product comes in. An MVP allows you to test your idea's potential, gather feedback, and iterate quickly, all while minimizing costs and maximizing your chances of success.
Building a Minimum Viable Product is a crucial step in the product development process. It helps you validate your idea, understand your target audience, and gather essential insights for future iterations. In this article, we will explore the key steps and strategies to successfully build an MVP that will set your startup on the path to success.
What is an MVP (Minimum Viable Product)?
When developing a new product or service, it's important to understand the concept of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). An MVP is a basic version of your product that has just enough features to satisfy early adopters and gather valuable feedback for future development.
The core functionality of an MVP is the key focus. It should address the primary problem or need that your product aims to solve. By prioritizing the essential features, you can quickly bring your product to market and start gathering feedback from potential customers.
The goal of an MVP is not to have a fully polished product, but rather to test your assumptions and validate your ideas. By launching an MVP, you can gather user feedback and insights that will help you refine and improve your product based on real-world usage.
To determine if an MVP is successful, it is important to define clear success metrics that align with the goals of the product and the business. These metrics can include user engagement, conversion rates, customer satisfaction, or any other key performance indicators that indicate progress towards product-market fit.
In conclusion, building a minimum viable product is a strategic approach to product development that focuses on delivering a basic version of a product with core features to gather feedback and validate assumptions. By starting with an MVP, businesses can iterate and refine their product based on real user interactions, increasing the chances of achieving product-market fit and long-term success.
Purpose of an MVP
The purpose of a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is to quickly test and validate the viability of a product idea with minimal resources and investment. It allows entrepreneurs and engineering teams to gather valuable feedback from early adopters and learn from real user interactions, enabling them to make informed decisions about the product's future development and potential market success.
By launching an MVP, entrepreneurs can also mitigate the risk associated with building a product that may not find a market fit. It allows them to validate their ideas early on, identify potential product-market fit issues, and make necessary adjustments before investing significant time and resources into a full-scale product development.
Moreover, an MVP serves as a powerful communication tool to engage potential investors, partners, and stakeholders. It demonstrates a tangible proof of concept and showcases the value proposition of the product, making it easier to secure funding, partnerships, or support for further development and growth.
Step 1: Do your research on the market
The first step in building a minimum viable product (MVP) is conducting thorough market research. This involves gathering information about your target market, competitors, and industry trends to gain a deep understanding of customer needs and preferences.
Market research helps you identify gaps in the market that your product can fill and allows you to validate your ideas before investing time and resources into development. By analyzing customer feedback and studying your competitors, you can identify opportunities and potential challenges that may arise.
To conduct market research effectively, you can use various methods such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and analyzing data from relevant sources. It is essential to gather both quantitative data, such as market size and customer demographics, and qualitative data, including customer pain points and preferences.
By thoroughly understanding your target market and competitors, you can tailor your MVP to meet the specific needs and expectations of your potential users. This step lays the foundation for a successful product development process and increases the likelihood of creating a product that resonates with your target users.
Step 2: Build an MVP based on value
When building an MVP let's start off with the basic, think about the customer's problem and overall pain points when trying to solve that problem. These will make up the limited functionality needed to be built out and tested. By focusing on key pain point features, overall development costs won't get out of control and the core basic features should be ironed out as real users try out the product and validate it's usefulness.
By understanding your target audience and their pain points, you can determine which features will address their needs most effectively. This requires conducting market research, gathering customer feedback, and analyzing user behavior to gain insights into what features will provide the most value. It should be at this stage that you can start to outline what you believe your competitive advantage will be. How will your solution be different from everyone else's? As the product owner, you'll be able to articulate the key differences and perhaps how a consumer gets a better bang-for-the-buck by switching to your solution.
Once you have identified the key features, it's important to keep the MVP simple and streamlined. Avoid adding unnecessary features that may complicate the development process or confuse users. Instead, focus on delivering the core value proposition of your product in the most efficient and effective way possible.
During the development process, it's crucial to maintain a strong feedback loop with your target audience. This involves regularly testing and iterating on your MVP based on user feedback. By gathering insights and making necessary adjustments, you can ensure that your MVP continues to provide value and meets the needs of your target audience.
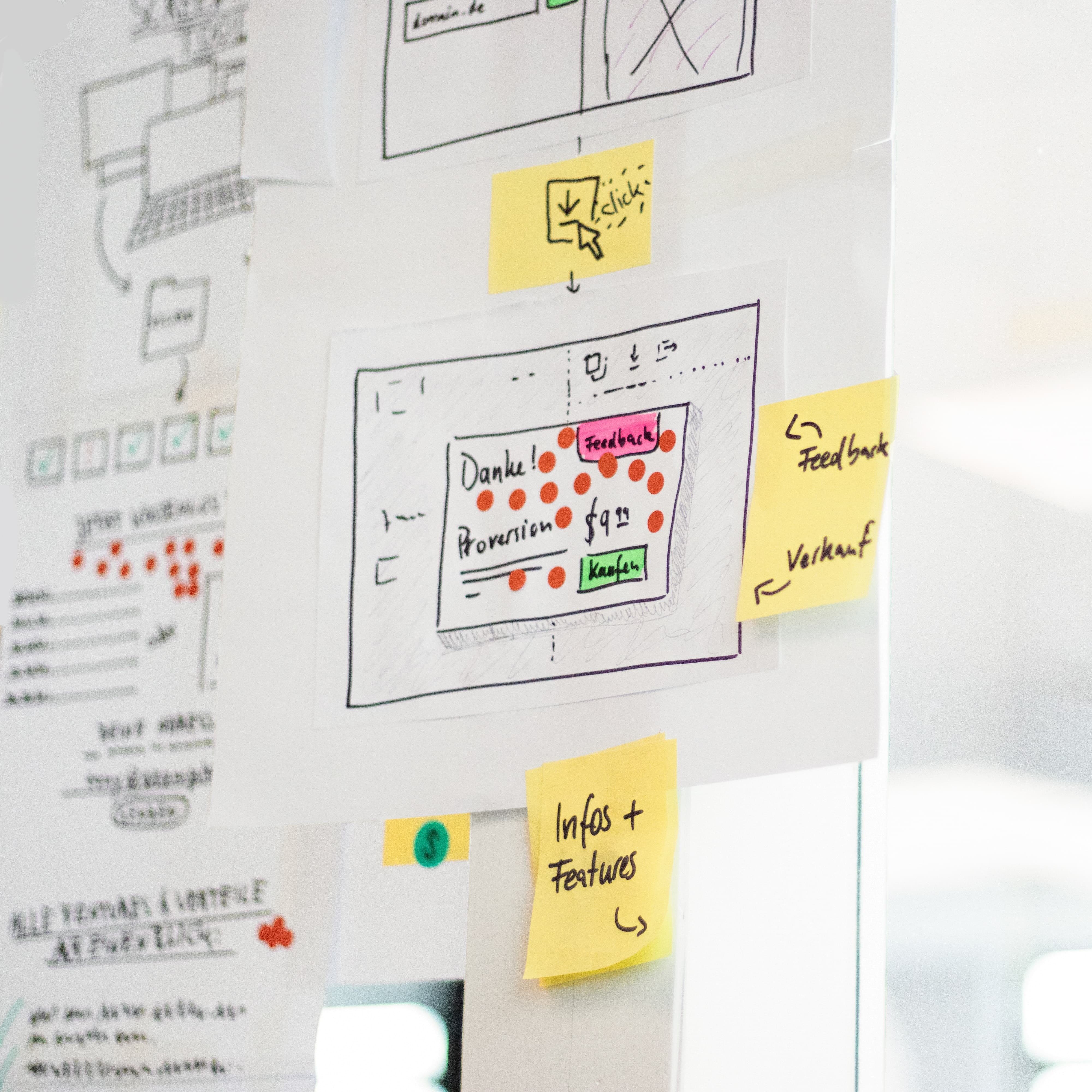
Step 3: Map out the user experience
As you start to put the MVP together it's important to map out the user flow, and the overall user experience. Having a weak user experience can cause users to only focus on the negatives instead of giving it a fair chance to solve their problem.
A User Journey Map is an overview of what screens the user will experience in what sequential order and the different user pathways that might take place depending on how the user engages with the features. UI/UX can be outsourced if necessary but keep things simple.
Remember this stage is about ensuring that the vital features are present, and the user flow needs to be intuitive enough and smooth enough that users are able to focus on validating if they are using a valuable product or if it's just a an awesome idea in theory but there's no real demand.
Start by identifying the key actions that users will need to take in order to achieve their goals. Break down these actions into smaller steps, and consider the logical order in which they should be presented.
Ensure that the user flow is intuitive and user-friendly, minimizing any confusion or friction that could hinder the user's progress. Incorporating user feedback and conducting usability testing can help identify any areas that need improvement in the user flow.
By mapping out the user flow, you can optimize the user experience and increase the chances of users successfully navigating through your MVP. This will ultimately lead to a better understanding of user needs and enable you to iterate and improve your product based on real user interactions.
This is more of a side note, but even as the internal team grows, it's important that the user experience is never forgotten and is held as a main priority when it comes to product creation and building out a wide range of future developments. This will ensure a core product that has a strong user experience, which will ultimately lead to a higher retention rate and loyal customers.
Step 4: Prioritize the 'must-have' features
When building a minimum viable product (MVP), it's crucial to prioritize the features that will provide the most value to your target audience. By focusing on the core functionalities of your product, you can quickly validate your idea and gather feedback from early adopters.
Next, categorize the features into "must-have," "nice-to-have," and "future enhancements." Must-have features are those that directly solve the core problem your product addresses and are essential for its basic functionality. Nice-to-have features can enhance the user experience, but are not critical for the initial version, these can be additional features down the line or in future products. Future enhancements can be added later based on user feedback and market demand.
Consider the complexity and development effort required for each feature. Focus on features that can be developed and launched quickly, allowing you to gather feedback and iterate on your product. Keep in mind that simplicity is key for an MVP, so prioritize features that can be implemented with minimal complexity and cost. The more complex the feature, you need to consider if the elongated development stage is a necessity, is this feature a 'must-have' or a 'nice-to-have'? The more complex and the more time that needs to go towards development also increases your overall development costs. Remember, you don't need a fully-featured product, but rather the minimum features required to solve their pain point and give you feedback if your product is better then the users' current solution.
Remember that your MVP should be a lean and stripped-down version of your final product. Prioritizing features ensures that you deliver the most valuable functionalities to your users, while also keeping development time and costs under control. It's important to continually reassess and prioritize features as you receive feedback and insights from your early adopters.
Step 5: Launch MVP
When launching your MVP, it's important to have a clear strategy in place. Start by identifying the most appropriate platform or channels to reach your target audience. Whether it's through your website, mobile app stores, or social media platforms, choose the channels that will give you the most visibility and accessibility to your potential users. If you're planning on launching a free MVP it'll be important during the launch phase to gather feedback and try to clarify time to market (when you'll start generating revenue). Remember, there are countless business ideas but launching the MVP is the define if you've got a viable product software.
Next, make sure to communicate the value proposition of your product effectively. Highlight the unique features and benefits that set your MVP apart from competitors. Clearly articulate how your product solves a specific problem or meets a particular need, and why users should choose your solution over others in the market. Just because you build it, doesn't mean people will automatically flock to your solution. Creating effective messaging that clearly identifies the value proposition that resonates with your target market will be critical.
During the launch phase, it's crucial to closely monitor user interactions and gather feedback. This will help you identify any issues or areas for improvement that may have been missed during the testing phase. Actively engage with your users, listen to their feedback, and use it to make iterative improvements to your MVP.
Additionally, consider implementing analytics tools to track user behavior and gather data on how users are interacting with your product. This data can provide valuable insights into user preferences, usage patterns, and areas of improvement, helping you refine your product and prioritize future development efforts.
Lastly, don't forget to promote your MVP through various marketing channels. Utilize social media platforms, content marketing, email campaigns, and other promotional strategies to generate awareness and attract potential users. Leverage your existing networks and partnerships to spread the word about your product and encourage early adoption.
By following these steps and effectively launching your MVP, you will be able to gather valuable user feedback, validate your product concept, and make informed decisions for future iterations and enhancements. Remember, the goal of launching an MVP is to quickly and cost-effectively test your product idea in the market, and use the insights gained to iterate and improve upon it.
Step 6: Making sense of the feedback
Upon a successful launch of your MVP it'll be critical to take in the initial feedback and start to translate that into action items that will need to take place and in what time frame.
The number one priority is to ensure that your MVP solves the pain ratio users are feeling, are they ultimately satisfied with what the MVP does? Are there key project requirements that are missing? This testing stage is ensure real user feedback is captured so that the internal team can make sense of it, and to create the 'what's next' phase and what kind of business goals is trying to get accomplished?
Next, analyze each piece of feedback to understand the underlying reasons behind it. Look for common pain points or needs that your users are expressing and consider how these align with your product's goals and value proposition.
After analyzing the feedback, it's important to take action and make necessary adjustments to your MVP. This may involve fixing bugs, addressing usability issues, or adding new features based on the feedback received.
Remember to involve your engineering team in the feedback analysis process, as they will have valuable insights and expertise to contribute. Collaborate with them to come up with effective solutions and determine the feasibility and impact of implementing changes.
Finally, communicate with your users and stakeholders about the changes you have made based on their feedback. This not only shows that you value their input but also helps build trust and loyalty among your user base. Keep an open line of communication to gather further feedback and continue improving your product. When a customer sees their input make it into a future product, this can go a long way in creating a stickiness factor, that's not just created by the user-experience but by also building an engaged user community.
5 Development Mistakes to Avoid While Building an MVP
1. Choosing the Wrong Problem to Solve
When building a minimum viable product (MVP), it is crucial to choose the right problem to solve. Many entrepreneurs make the mistake of focusing on a problem that is not significant enough or does not have a market demand. This can lead to wasted time, effort, and resources.
One of the first steps in the pre-MVP stage is conducting thorough research. You need to identify the pain points that your target audience is experiencing and determine if your solution can effectively address these pain points. By understanding the needs and desires of your potential customers, you can ensure that you are solving a problem that is both valuable and relevant.
However, even with extensive research, it is still possible to choose the wrong problem to solve. This can happen if you misinterpret the data or overlook important factors. It is essential to validate your assumptions and gather feedback from your target audience throughout the research process.
Choosing the wrong problem to solve can have serious consequences. It can result in a product that no one wants or needs, leading to poor sales and a failed business. Additionally, it can hinder your ability to attract investors or secure funding.
To avoid this mistake, take the time to thoroughly analyze the data and insights gathered during your research. Look for patterns and trends that indicate a significant problem that needs to be solved. Consider conducting surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gain a deeper understanding of your target audience's pain points.
Furthermore, engage in continuous learning and iteration. As you develop your MVP, be open to feedback and willing to make adjustments if necessary. This will help ensure that you are building a product that truly addresses the needs of your target audience.
2. Skipping the Prototype Phase
One common mistake when building a minimum viable product (MVP) is skipping the prototype phase. The prototype phase is crucial for testing and validating your product before investing too much time and resources into development. By skipping this phase, you risk falling victim to wasting valuable time and effort. It's during this project discovery phase whereby including user feedback at an early stage can help you flesh out what's needed in the core product.
The prototype phase allows you to gather feedback from potential users and stakeholders early on. It helps you validate your assumptions and make informed decisions about the features to include in your MVP. By involving users in the testing process, you can gain valuable insights and ensure that your product aligns with their needs and expectations.
Additionally, by starting with a prototype, you can save time in the long run. It allows you to focus on building the minimum set of features required to deliver value to your users. This approach follows the principle of minimum time, maximum learning, and iterative development. Instead of spending months or years developing a product only to find out it doesn't meet market demand, you can iterate and improve based on user feedback gathered during the prototype phase.
3. Targeting the Wrong Segment of Persona
One common mistake that entrepreneurs often make when building a minimum viable product (MVP) is targeting the wrong segment of persona. Your target market is the group of customers who will benefit the most from your product or service. If you fail to identify and understand your target market correctly, you risk wasting time, money, and effort on developing a product that doesn't resonate with your customers.
One aspect to consider when identifying your target market is the range of customers you can potentially serve. It's important to analyze the different customer segments that might be interested in your product and evaluate their specific needs, preferences, and pain points. Conducting market research and gathering customer feedback can help you gain insights into the various customer segments and identify the most promising ones to target.
Another mistake is blindly assuming that your target market will be willing to adopt your product. It's crucial to challenge your assumptions by validating your product with potential customers. This can be done through surveys, interviews, or even building a prototype to gather feedback and gauge interest. By involving your target market early on in the development process, you can ensure that you are building a product that solves their problems and meets their needs.
Lastly, targeting the wrong segment of persona can lead to missed opportunities. By focusing on the wrong target market, you might overlook other potential customer segments that could greatly benefit from your product. It's important to continually evaluate and reassess your target market to identify any new or emerging segments that might be interested in your offering.
5. Understanding qualitative and quantitative Feedback
When building a minimum viable product (MVP), one common mistake that many entrepreneurs make is confusing qualitative and quantitative feedback. Understanding the difference between these two types of feedback is crucial for the success of your product.
Qualitative feedback refers to subjective opinions, experiences, and emotions expressed by users. It provides insights into the user's perspective, allowing you to understand their needs, pain points, and preferences. This feedback usually comes in the form of user interviews, surveys, or usability testing.
On the other hand, quantitative feedback involves collecting numerical data and metrics to analyze user behavior and patterns. It helps you measure the performance of your product and identify trends or patterns. Common sources of quantitative feedback include analytics tools, A/B testing, and metrics such as conversion rates, bounce rates, or time on page.
The mistake occurs when entrepreneurs solely rely on one type of feedback and neglect the other. For example, if you only focus on collecting qualitative feedback, you might gather a lot of opinions and stories from users but lack concrete data to validate their claims. Similarly, solely relying on quantitative feedback might lead you to make decisions solely based on numbers without understanding the underlying user experience.
To avoid this mistake, it is important to strike a balance between qualitative and quantitative feedback. Combine user interviews, surveys, and usability testing to gather qualitative insights about what features users find useful or frustrating. This will give you a list of killing features that you can prioritize in your MVP development. However, the balance of this sentiment is to avoid feature creep, which is the tendency to get locked into adding additional features.
At the same time, use analytics tools, A/B testing, and metrics to collect quantitative data on user behavior. This will help you understand how users interact with your product, identify areas of improvement, and validate the impact of the features you have implemented.
By using both qualitative and quantitative feedback, you will have a comprehensive understanding of your target users and their needs. This will enable you to make informed decisions when prioritizing features, refining your product's feature mix, and ultimately building a successful minimum viable product.
Measuring Success After Building an MVP
2. Engagement
Once of the key measurements to keep track of as you gather user feedback is their overall engagement, and how they engage with the product. When building a minimum viable product (MVP) for your product, it's important to focus on metrics that measure engagement. These metrics will give you insights into how users are interacting with your app and whether it is meeting their needs effectively. By tracking these metrics, you can make informed decisions on how to improve your app and increase its growth rate.
One key metric to focus on is user retention. This measures the percentage of users who continue to use your app over a specific period of time. A high user retention rate indicates that users find value in your app and are likely to continue using it. To improve user retention, you can analyze user feedback and make necessary improvements to enhance the user experience.
Another important metric is session duration, which measures the average length of time users spend in each session. A longer session duration indicates that users are engaged and finding value in your app. By analyzing this metric, you can identify features or content that are keeping users engaged and optimize your app accordingly.
Additionally, tracking the number of active users can give you insights into the overall growth rate of your app. This metric measures the number of unique users who are actively using your app within a specific time frame. A steady increase in active users indicates that your app is gaining traction and attracting new users.
If you're trying to get a consumer to do a certain action, it'll be relevant to track your conversion rate: this metric measures the percentage of users who take a desired action, such as signing up for a newsletter or making a purchase. Tracking conversion rate helps you understand how effective your MVP is at driving user actions and achieving your business goals.
By focusing on these engagement metrics, you can identify areas of improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance your MVP. Use tools like analytics platforms or user feedback to gather the necessary data and regularly analyze the metrics to track progress and iterate on your product.
Lastly, consider analyzing user behavior within your app, such as the number of screens visited or actions taken. This can help you understand how users navigate through your app and identify any pain points or areas for improvement.
It's one thing to dream up product creation, it's another to actually create a valuable product a user is willing to come back to. If you're not seeing the overall engagement you want to see, there's a wide range of potential 'what ifs' for you to consider; it could be the pain point isn't important enough to your target market, the product isn't user intuitive or (too painful to use) whereby your might want to engage with the engineering team and looking at design services to ensure the user experience is improved.
You'll also need to be fair that when you initially launch, if it's not marketing well the engagement can't be expected to be any better. You need to have a sizeable enough user base to gather a fair amount of feedback including their engagement and overall user experience. So you might see a ramp up in terms of engagement depending on how you're acquiring users.
3. Sign-Up
The sign-up rate measures the number of users who successfully register or create an account on your platform or app. This metric is crucial as it indicates the initial interest and willingness of users to engage with your product. Here are some considerations for optimizing the sign-up process and improving your sign-up rate:
1. Intuitive UX Design: A seamless and intuitive user experience is essential for encouraging sign-ups. Ensure that the registration process is straightforward, with clear instructions and minimal steps. Avoid asking for excessive information upfront, as this may deter users from completing the sign-up process. Keep the design clean and visually appealing to enhance user engagement.
2. Clear Value Proposition: Clearly communicate the value and benefits users can expect from signing up. Highlight any unique features or advantages of your SaaS product or app that will solve their pain points or meet their needs. Conveying a compelling value proposition will increase the motivation for users to join and explore your offering. Ensuring your value proposition is clearly communicated to a specific target persons will also enable you to validate if you're going after the right niche.
3. Streamlined Sign-Up Flow: Eliminate any unnecessary barriers or friction in the sign-up process. Minimize the number of required fields and streamline the process by utilizing social media login options or pre-filled form fields. Offering multiple sign-up methods and ensuring compatibility across different devices and platforms will cater to a wider audience and boost sign-up rates. A completely new and innovative product that someone is unfamiliar with and don't have anything to compare it to, can also make it seem intimidating or needing to be educated.
4. Effective Call-to-Action: Use persuasive and visually appealing call-to-action buttons or links to prompt users to sign up. The wording should be clear, concise, and action-oriented, encouraging users to take the desired action. Experiment with different placement and design options to optimize the visibility and click-through rate of your sign-up call-to-action.
5. Analyze and Optimize: Continuously analyze the sign-up metrics to identify any bottlenecks or areas for improvement. Utilize analytics tools to track user behavior, drop-off points, and conversion rates. A/B testing different variations of the sign-up process can help you identify the most effective strategies for increasing sign-up rates.
By focusing on the sign-up metric and implementing strategies to optimize this step, you can ensure that your MVP successfully converts those that use the app into users. This will provide a solid foundation for further user engagement and feedback, enabling you to iterate and improve your product based on real user data.
5. Percentage of active users
When building a minimum viable product (MVP), it's crucial to define success metrics to measure the effectiveness and engagement of your product. One important success metric to consider is the percentage of active users.
The percentage of active users refers to the proportion of users who regularly interact with your MVP. These are the users who not only sign up or download your product but also actively engage with it on a consistent basis. Tracking this metric allows you to gauge the level of interest and satisfaction among your user base.
To effectively measure the percentage of active users, you need to establish a baseline and set specific goals. Start by defining what "active" means for your product. It could be logging in a certain number of times per week, completing specific actions within the product, or any other relevant user engagement metric.
Regularly monitor the percentage of active users and analyze any changes or trends. If the percentage is low or declining, it may indicate that users are not finding value in your MVP or encountering difficulties in using it. In such cases, it's crucial to identify the underlying issues and make necessary improvements to increase user engagement.
On the other hand, if the percentage of active users is high or increasing, it signifies that your MVP is resonating with your target audience. This is a positive indication that your product is meeting user needs and delivering value.
By focusing on the percentage of active users as a success metric, you can continuously iterate and improve your MVP to ensure it aligns with user expectations. It provides valuable insights into user behavior, preferences, and satisfaction, allowing you to make data-driven decisions and optimize your product updates for long-term success.
Advanced users are those who have fully explored and utilized the features and functionalities of your MVP. They are the ones who have moved beyond the initial onboarding stage and have become proficient in using your product. Tracking the percentage of advanced users can provide valuable insights into the level of engagement and satisfaction among your user base.
To measure this metric, you can set specific criteria that define an advanced user. For example, an advanced user might be someone who has completed a certain number of tasks or has accessed specific advanced features. By setting clear criteria, you can accurately track the percentage of users who have reached this advanced level.
Monitoring the percentage of advanced users is crucial because it indicates the success of your product in retaining and satisfying users over time. A high percentage suggests that users find value in your product and are motivated to explore its advanced features. On the other hand, a low percentage may indicate usability issues or a lack of engagement, requiring you to make improvements to enhance the user experience.
6. Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Customer acquisition cost refers to the amount of money you spend on acquiring each new customer. This metric is crucial because it directly impacts your profitability. If your CAC is too high, it can eat into your revenue and make it difficult to generate profits.
To calculate CAC, you need to take into account all the costs associated with acquiring customers. This includes marketing and advertising expenses, sales team salaries, and any other external and internal costs incurred in the process of attracting and converting customers.
Once you have calculated your CAC, you can compare it to the lifetime value of your customers (LTV). LTV is the estimated revenue a customer will generate over their lifetime as a customer. If your CAC is significantly higher than your LTV, it may indicate that your marketing and acquisition strategies need to be adjusted. Customer-acquisition-cost ratio with LTV can also be measured as CLV:CAC, which as a general rule of thumb is usually with a target of 3:1 ratio (or, it means you're spending approximately 33% of the average LV on acquiring new customers).
Lowering your CAC can be achieved through various tactics. One effective approach is to optimize your marketing channels and campaigns. By analyzing data and identifying the most cost-effective channels, you can allocate your marketing budget more efficiently and reduce your CAC.
Another strategy is to improve your conversion rate. By optimizing your website or product landing pages, streamlining the purchasing process, and providing a seamless user experience, you can increase the number of customers acquired from your marketing efforts, thus reducing your CAC.
It's important to regularly monitor and analyze your CAC to ensure that your marketing efforts are generating a positive return on investment. By continuously optimizing your customer acquisition strategies, you can improve your product's profitability and drive the growth of your business.
7. Number of Paying Users
When building a minimum viable product (MVP), it is important to consider the number of paying users as a crucial aspect of your product pricing strategy. The number of paying users directly impacts your revenue and the success of your business.
Firstly, you need to determine your target market and understand the size of the mass market that your product caters to. This will help you estimate the potential number of paying users you can acquire. Conduct market research to identify the demand for your product and gather insights into customer preferences and pricing expectations.
Next, consider the pricing model for your MVP. If you opt for a subscription-based pricing strategy, you'll need to determine the subscription prices that will attract and retain paying users. Analyze the pricing strategies of your competitors to ensure your prices are competitive and provide value to your customers.
Additionally, it is essential to consider the average revenue you can generate per person per month. This metric helps you estimate your monthly revenue based on the number of paying users. Calculate your break-even point and set realistic revenue goals to ensure sustainability and profitability.
To attract a higher number of paying users, consider offering incentives such as discounts for annual subscriptions, referral programs, or limited-time promotions. These strategies can help increase your user base and generate more revenue.
Regularly monitor and analyze your number of paying users to identify trends and make data-driven decisions. If you notice a decline in paying users, it may be necessary to reevaluate your pricing strategy, improve your product, or enhance your marketing efforts.
Remember that building a minimum viable product is just the beginning. As you gather feedback and iterate on your product, continuously evaluate and adjust your pricing strategy to align with the needs and expectations of your target market and maximize your revenue potential. What's important in the early stages is understanding is you're able to build and maintain a viable product software. You'll need to constantly keep track of overall cost of production, price of components, and what revenue can be generated from paying users.
9. Churn Rate
When building a minimum viable product (MVP), it's crucial to measure churn rate. Churn rate refers to the percentage of customers who stop using your product or service over a given period of time. It is a key metric that helps you understand the effectiveness of your current solution and identify areas for improvement.
Measuring churn rate allows you to gather valuable feedback from customers who have decided to discontinue using your product. By analyzing the reasons behind their departure, you can gain insights into the shortcomings of your MVP and make necessary adjustments. Negative feedback from churned customers can serve as a valuable source of information to enhance your product and retain more customers in the future.
Additionally, measuring churn rate helps you price intelligently. If your churn rate is high and customers are leaving due to pricing issues, it may indicate that your product is overpriced or not providing enough value for the price. By understanding the correlation between churn rate and pricing, you can make informed decisions about adjusting your pricing strategy to better align with customer expectations.
Let's take a brief second to define common pricing strategies:
One effective pricing strategy for an MVP is the "freemium" model, where you offer a basic version of your product for free and charge for additional features or premium versions. This allows you to attract a larger user base initially and then monetize through upselling or offering additional services.
Another strategy is to adopt a value-based pricing approach, where you set the price based on the perceived value your product provides to customers. This requires thorough market research and understanding your customers' willingness to pay for the benefits your product offers.
Cost-plus pricing is a pricing strategy commonly used when building a minimum viable product (MVP). It involves calculating the total cost of production, including direct costs like materials and labor, as well as indirect costs like overhead expenses. Once the total cost is determined, a markup or profit margin is added to ensure profitability.
Alternatively, you can choose a penetration pricing strategy, where you initially set a low price to quickly gain market share and attract early adopters. This strategy aims to create buzz and generate word-of-mouth marketing, helping your MVP gain traction in the market.
Lastly, you could consider a dynamic pricing strategy, where you adjust the price of your MVP based on factors such as demand, competition, or customer behavior. This allows you to optimize pricing based on real-time market conditions and maximize revenue.
Regardless of the pricing strategy you choose, it is important to continuously analyze and assess its effectiveness. Collect feedback from customers, monitor market trends, and make adjustments as necessary to ensure your pricing aligns with the value your MVP delivers as well ensuring you're able to execute target actions and achieve your business goals.
You might not be price ready when building your MVP, the main purpose of the MVP is to validate the core product's feature set and if there's a demand for your solution. However, it's not a bad thing to start to think about how you're going to monetize your product. Pricing strategy is a mixture of an art and science, there's the 'what I need to charge to cover expenses' and 'what customers believe is a fair price to pay'... and these aren't always aligned with one another.
Stay connected with news and updates!
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.
Don't worry, your information will not be shared.
We hate SPAM. We will never sell your information, for any reason.